by Susan Flantzer
© Unofficial Royalty 2021

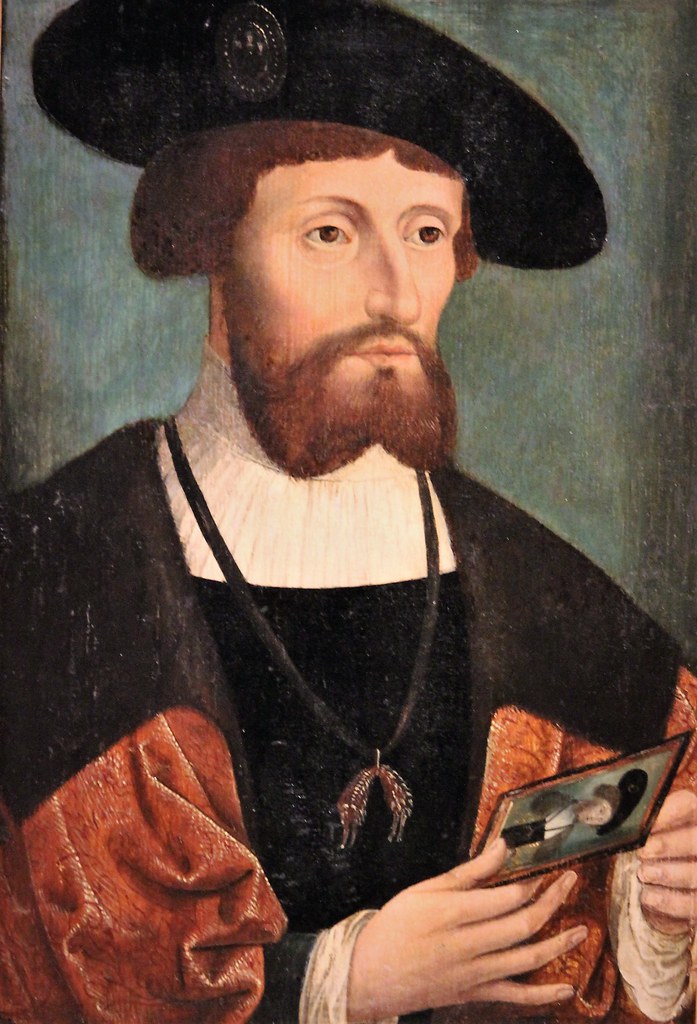
Christian III, King of Denmark and Norway; Credit – Wikipedia
The only son and the elder of the two children of Frederik I, King of Denmark and Norway and his first wife Anna of Brandenburg, Christian III, King of Denmark and Norway was born on August 12, 1503, at Gottorp Castle in Schleswig, Duchy of Schleswig, now in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein.
Christian had one younger sister:
- Dorothea of Denmark, Duchess of Prussia (1504 – 1547), married Albrecht of Brandenburg-Ansbach, Duke of Prussia, had six children

Christian III’s parents Frederik I and Anna of Brandenburg; Credit – Wikipedia
Having two children during her teenage years weakened the health of Christian’s mother. She contracted tuberculosis and died on May 3, 1514, aged 26, while six months pregnant. Four years after the death of his mother Christian and his sister Dorothea got a stepmother when their father married Sophie of Pomerania on October 9, 1518.
Christian had six half-siblings from his father’s second marriage:
- Johann II, Duke of Schleswig-Holstein-Haderslev (1521 – 1580), unmarried
- Elisabeth of Denmark (1524 – 1586), married (1) Magnus III, Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, no children (2) Ulrich III, Duke of Mecklenburg-Güstrow, had one daughter
- Adolf of Denmark, Duke of Holstein-Gottorp (1526 – 1586), married Christine of Hesse, had ten children
- Anna of Denmark (1527 – 1535), died in childhood
- Dorothea of Denmark (1528 – 1575), married Christof, Duke of Mecklenburg-Gadebusch, no children
- Frederik of Denmark, Prince-Bishop of Hildesheim and Bishop of Schleswig (1532 – 1556), unmarried

Martin Luther at the Diet of Worms; Credit – Wikipedia
Christian grew up during the time of the Protestant Reformation. He first encountered the teachings of Martin Luther from his tutor Wolfgang von Utenhof. In 1521, when he was 18-years-old, Christian traveled to the Imperial Free City of Worms, now in Germany, to witness the Diet of Worms, an assembly of the Holy Roman Empire, called by Holy Roman Emperor Charles V. Pope Leo X had warned Martin Luther that unless he recanted his reformer views, he risked excommunication. Martin Luther had been summoned to renounce or reaffirm his views. He defended his reformer views and refused to recant them. Holy Roman Emperor Charles V then issued the Edict of Worms that condemned Martin Luther as “a notorious heretic” and banned citizens of the Holy Roman Empire from propagating his ideas.
Martin Luther’s performance at the Diet of Worms made a great impression on Christian and impacted his future. When he returned home, Christian made no secret of his Lutheran views. Christian’s father became King in 1523 and his father gave him the management of part of the Duchies of Schleswig and Holstein. In 1528, Christian officially introduced Lutheranism into the duchies. This brought him into conflict, not only with the Catholic-dominated State Council but also with his father. His father Frederik I was the last Roman Catholic Danish monarch. All subsequent Danish monarchs have been Lutheran. Although Frederik remained Catholic, he was somewhat tolerant of the new Protestant Lutheran religion. He ordered that Lutherans and Roman Catholics share the same churches and encouraged the first publication of the Bible in the Danish language. When Lutheran reformer Hans Tausen was threatened with arrest and trial for heresy, Frederick appointed him his personal chaplain to give him immunity. Frederik’s attitude toward religion postponed the all-out warfare between Protestants and Roman Catholics that occurred during the reign of his son King Christian III and that ultimately turned Denmark into a Protestant nation.

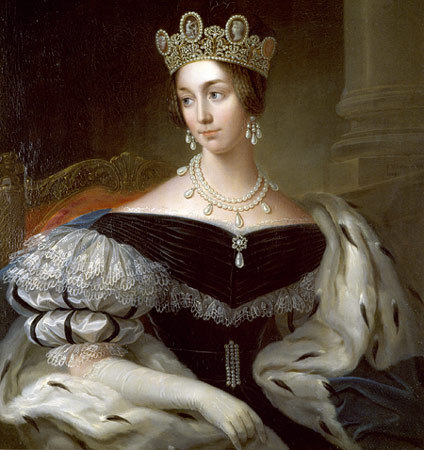
Christian III’s wife Dorothea of Saxe-Lauenburg; Credit – Wikipedia
On October 29, 1525 at Lauenburg Castle in Lauenberg, Duchy of Saxe-Lauenberg, now in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein, Christian married Dorothea of Saxe-Lauenburg, daughter of Magnus I, Duke of Saxe-Lauenburg and Catherine of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel.
Christian and Dorothea had five children:
- Anna of Denmark (1532 – 1585), married Augustus, Elector of Saxony, had fifteen children
- Frederik II, King of Denmark and Norway (1534 – 1588), married Sophie of Mecklenburg-Güstrow, had seven children including Christian IV, King of Denmark and Norway and Anne of Denmark, wife of James VI, King of Scots, later also King James I of England
- Magnus of Denmark, Duke of Holstein (1540 – 1583), married Maria Vladimirovna of Staritsa, had two children
- Hans II, Duke of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg (1545 – 1622), married (1) Elisabeth of Brunswick-Grubenhagen, had fourteen children (2) Agnes Hedwig of Anhalt, had nine children
- Dorothea of Denmark (1546 – 1617), married Wilhelm, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg, had fifteen children
After a reign of ten years, Christian’s father Frederik I, King of Denmark and Norway died on April 10, 1533, aged 61. After Frederik I’s death, the Danish Council of State had a lengthy discussion on whether the Danish throne should go to Christian, Frederik I’s Lutheran son from his first marriage, or Frederik I’s Catholic twelve-year-old son Johann from his second marriage. In 1534, Christian was proclaimed Christian III, King of Denmark at an assembly of Lutheran nobles in Jutland. However, the Danish Council of State, made up of mostly Catholic bishops and nobles, refused to accept Christian III as king. Johann, Frederik’s son from his second marriage, was deemed too young and the council was more amenable to restoring the deposed King Christian II to the throne because he had supported both the Catholics and Protestant Reformers at various times.
Christopher, Count of Oldenburg, the grandson of a brother of King Christian I of Denmark and the second cousin of both Christian II and Christian III, led the military alliance to restore King Christian II to the throne. What resulted was a two-year civil war, known as the Count’s Feud, from 1534 – 1536, between Protestant and Catholic forces, that led to King Frederik I’s son from his first marriage ascending the Danish throne as King Christian III. In 1537, Christian III was also recognized as King of Norway.
On August 12, 1536, King Christian III had three Catholic bishops arrested, partly to break the resistance to the Reformation and partly to pay off the debts by expropriating church property. Christian’s Protestant policies led Denmark to the establishment of Lutheranism as the Danish National Church on October 30, 1536, when the State Council adopted the Lutheran Ordinances designed by German theologian Johannes Bugenhagen, a close associate of Martin Luther.

Sophie of Pomerania, Christian III’s stepmother; Credit – Wikipedia
King Christian III had a long dispute with his widowed stepmother Sophie of Pomerania about her property. First, Christian II claimed Gottorp Castle for himself and forced Sophia to retire to Kiel Castle. Sophie considered the lands that her husband had bestowed upon her as her private property and she had continued conflicts with Christian III and his son and successor Frederik II over revenue management and the appointment of civil servants.

Tomb of King Christian III and Dorothea of Saxe-Lauenburg – Photo by Susan Flantzer
Christian III, King of Denmark and Norway died on January 1, 1559, aged 55, at Koldinghus, a Danish royal castle, on the Jutland Peninsula in Kolding, Denmark. He was buried in the Chapel of the Magi at Roskilde Cathedral in Roskilde, Denmark in a tomb designed by Flemish sculptor Cornelis Floris de Vriendt. His wife Dorothea survived him by twelve years, dying on October 7, 1571, aged 60, and was buried with her husband.
This article is the intellectual property of Unofficial Royalty and is NOT TO BE COPIED, EDITED, OR POSTED IN ANY FORM ON ANOTHER WEBSITE under any circumstances. It is permissible to use a link that directs to Unofficial Royalty.
Kingdom of Denmark Resources at Unofficial Royalty
- Kingdom of Denmark Index
- Danish Orders and Honours
- Danish Royal Burial Sites: House of Oldenburg, 1448 – 1863
- Danish Royal Burial Sites: House of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg, 1863 – present
- Danish Royal Christenings
- Danish Royal Dates
- Danish Royal Residences
- Danish Royal Weddings
- Line of Succession to the Danish Throne
- Profiles of the Danish Royal Family
Works Cited
- Da.wikipedia.org. 2021. Christian 3. – Wikipedia, den frie encyklopædi. [online] Available at: <https://da.wikipedia.org/wiki/Christian_3.> [Accessed 2 April 2021].
- De.wikipedia.org. 2021. Christian III. (Dänemark und Norwegen) – Wikipedia. [online] Available at: <https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Christian_III._(D%C3%A4nemark_und_Norwegen)> [Accessed 2 April 2021].
- En.wikipedia.org. 2021. Christian III of Denmark – Wikipedia. [online] Available at: <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Christian_III_of_Denmark> [Accessed 2 April 2021].
- Flantzer, Susan, 2021. Frederik I, King of Denmark and Norway. [online] Unofficial Royalty. Available at: <https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/frederik-i-king-of-denmark-and-norway/> [Accessed 2 April 2021].
- Flantzer, Susan, 2021. Sophie of Pomerania, Queen of Denmark and Norway. [online] Unofficial Royalty. Available at: <https://www.unofficialroyalty.com/sophie-of-pomerania-queen-of-denmark-and-norway/> [Accessed 2 April 2021].